Decentralized and Communication-Free Multi-Robot Navigation through Distributed Games (Submitted to ICRA 2022)
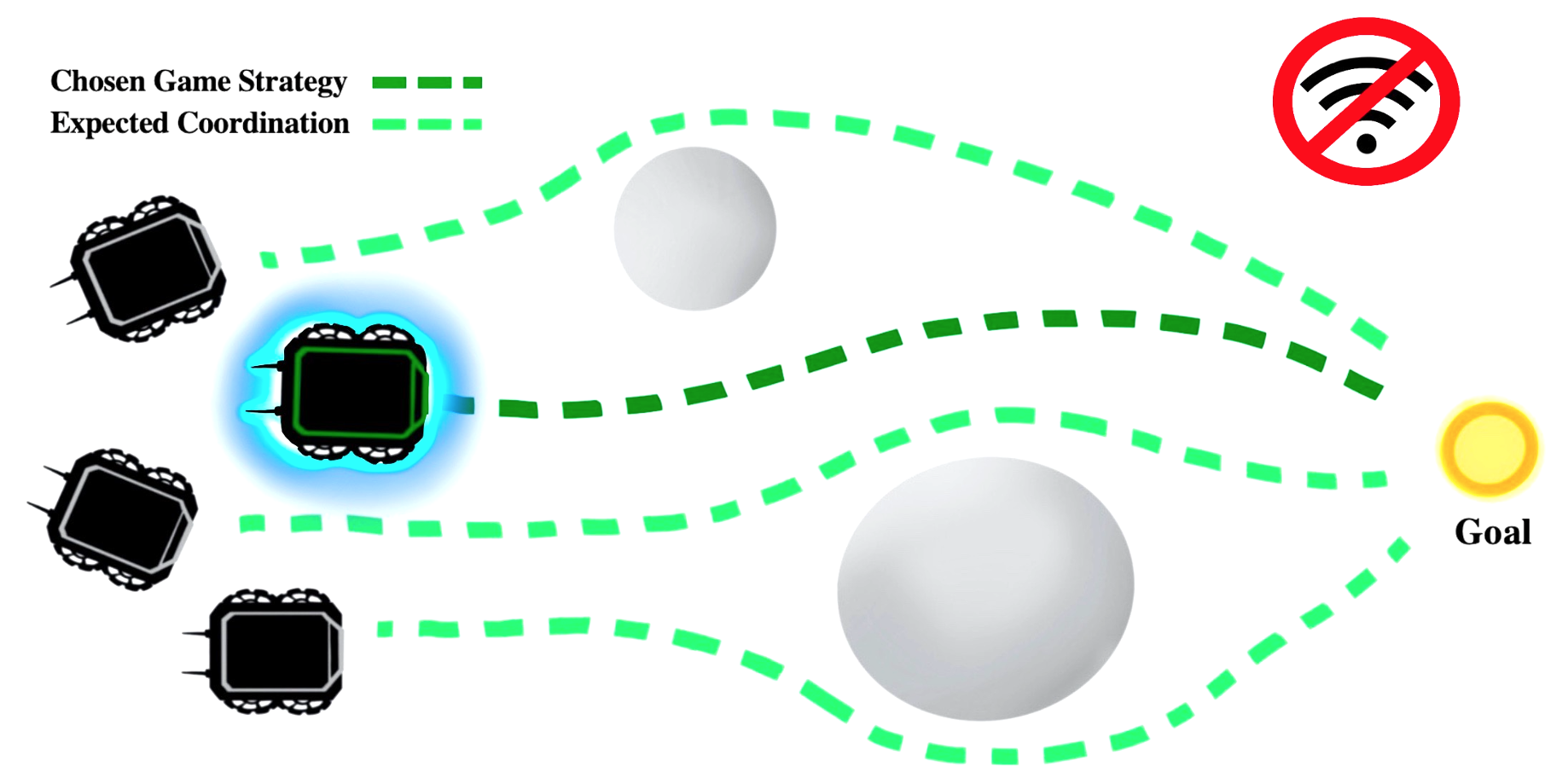
Effective multi-robot teams require the ability to move to goals in complex environments in order to address real-world applications such as search and rescue. Multi-robot teams should be able to operate in a completely decentralized manner, with individual robot team members being capable of acting without explicit communication between neighbors. In this paper, we propose a novel game theoretic model that enables decentralized and communication-free navigation to a goal position. Robots each play their own distributed game by estimating the behavior of their local teammates in order to identify behaviors that move them in the direction of the goal, while also avoiding obstacles and maintaining team cohesion without collisions. We prove theoretically that generated actions approach a Nash equilibrium, which also corresponds to an optimal strategy identified for each robot. We show through extensive simulations that our approach enables decentralized and communication-free navigation by a multi-robot system to a goal position, and is able to avoid obstacles and collisions, maintain connectivity, and respond robustly to sensor noise.
Citation: Decentralized and Communication-Free Multi-Robot Navigation through Distributed Games. Brian Reily, Terran Mott, and Hao Zhang. International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Submitted 2021.