Representing Multi-Robot Structure through Multimodal Graph Embedding for the Selection of Robot Teams (ICRA 2020)
[pdf] [video] [slides] [bibtex]
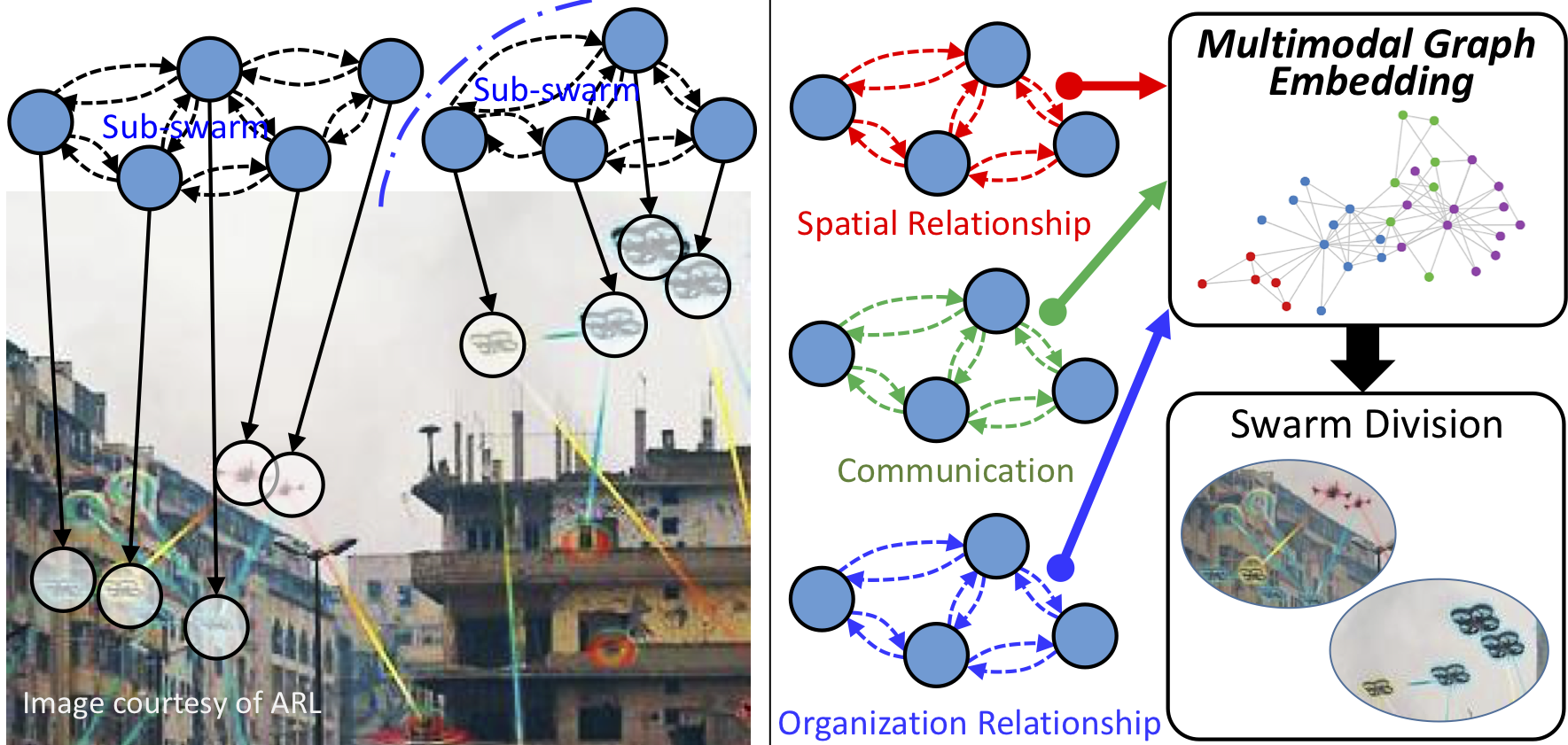
Multi-robot systems of increasing size and complexity are used to solve large-scale problems, such as area exploration and search and rescue. A key decision in human-robot teaming is dividing a multi-robot system into teams to address separate issues or to accomplish a task over a large area. In order to address the problem of selecting teams in a multi-robot system, we propose a new multimodal graph embedding method to construct a unified representation that fuses multiple information modalities to describe and divide a multi-robot system. The relationship modalities are encoded as directed graphs that can encode asymmetrical relationships, which are embedded into a unified representation for each robot. Then, the constructed multimodal representation is used to determine teams based upon unsupervised learning. We perform experiments to evaluate our approach on expert-defined team formations, large-scale simulated multi-robot systems, and a system of physical robots. Experimental results show that our method successfully decides correct teams based on the multifaceted internal structures describing multi-robot systems, and outperforms baseline methods based upon only one mode of information, as well as other graph embedding-based division methods.
Citation: Representing Multi-Robot Structure through Multimodal Graph Embedding for the Selection of Robot Teams. Brian Reily, Christopher Reardon, and Hao Zhang. International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2020.